There are several ways to start, stop and restart the MySQL server depending upon the operating system you are using. In this tutorial, we’ll learn how to start-stop and restart MySQL servers in windows, mac, and Linux operating systems.
Start, Stop and Restart MySQL Server on Windows
There are 3 ways by which you can perform these tasks on the MySQL server on Windows:
- Using services.msc
- Using Command Prompt
- Using MySQL Workbench
We’ll learn all three methods one by one:
Using services.msc
Step 1: On the keyboard press Windows, Type run on the search area, and click on open:
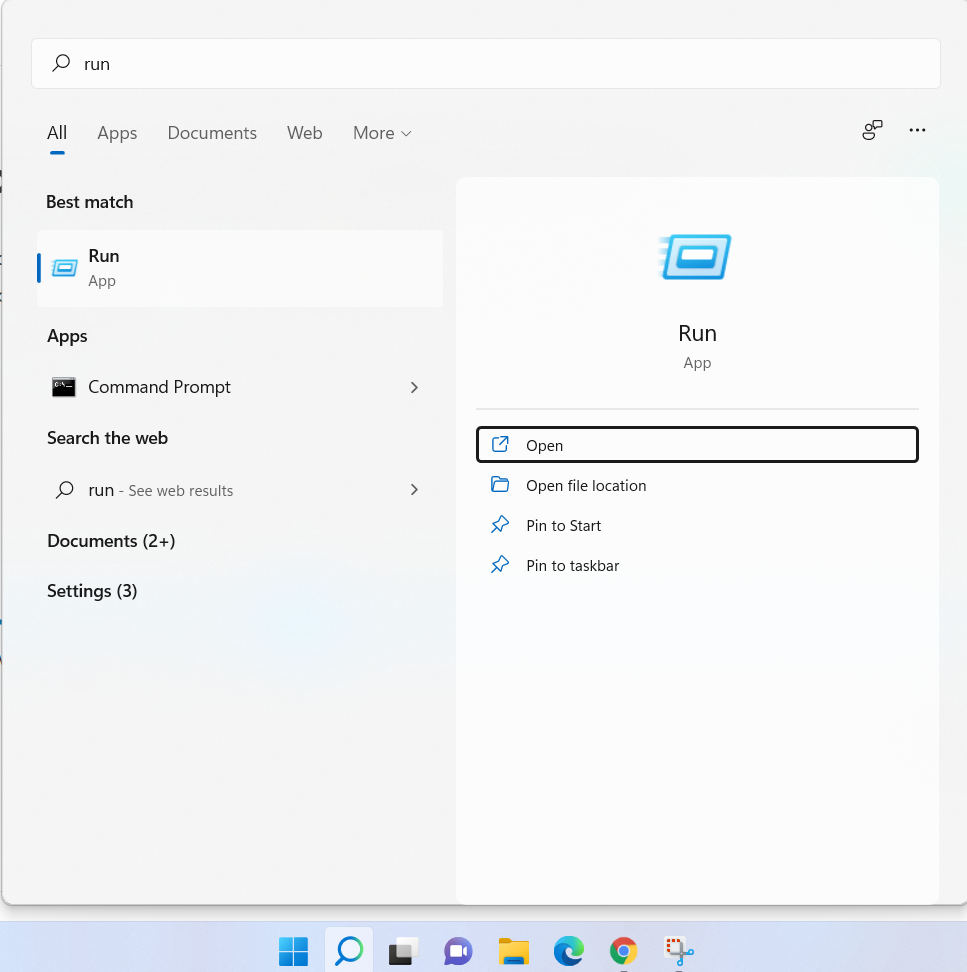
Step 2: Type Services.msc on run and click on OK:
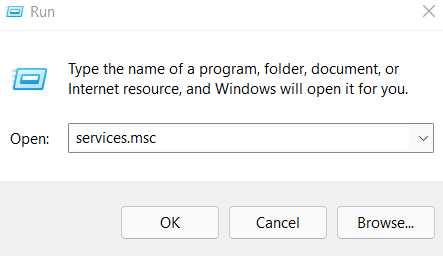
Step 3: Search for MySQL under the name column, Please keep in mind that the numeric extension after MySQL, as in the below example is MySQL80 may vary depending on the version of MySQL installed on your desktop. You can click on the MySQL80 section and a section on the left-hand side will be available to you with all the operations you can perform on that service.
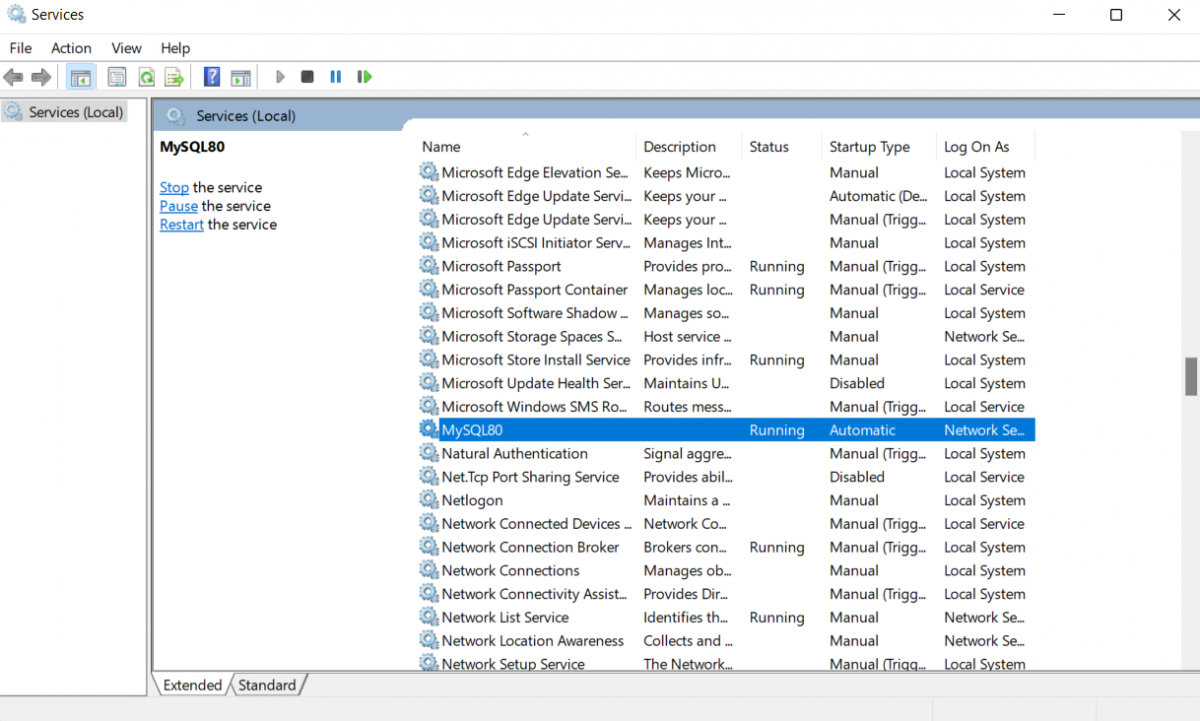
Step 4: Currently MySQL server is running, you can either choose to start, stop and restart the service from the left-hand side panel by selecting any of the options, or you can right-click on MySQL80 service and restart or stop the MySQL server from there.
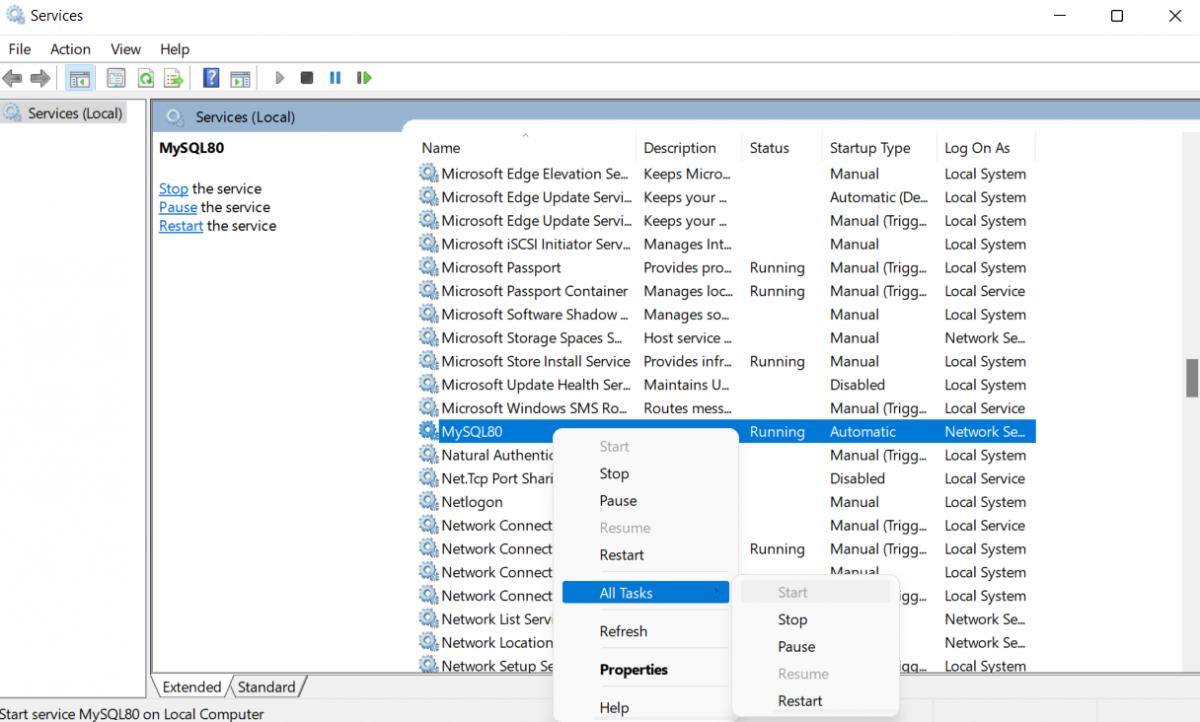
That’s how you can start, stop or restart the MySQL server in windows using services.
Using Windows Command Line
Step 1: Open Command Prompt, you can open it by pressing the Windows key on your keyboard and typing cmd on the search area.
Step 2: Start, stop or restart the MySQL server.
To stop the MySQL server you can type the following command:
net stop MySQL80Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)To start the MySQL server you can type the following command:
net start MySQL80Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Using MySQL Workbench
Step 1: Press the Windows key on your keyboard, type MySQL Workbench on the search bar, and open MySQL Workbench.
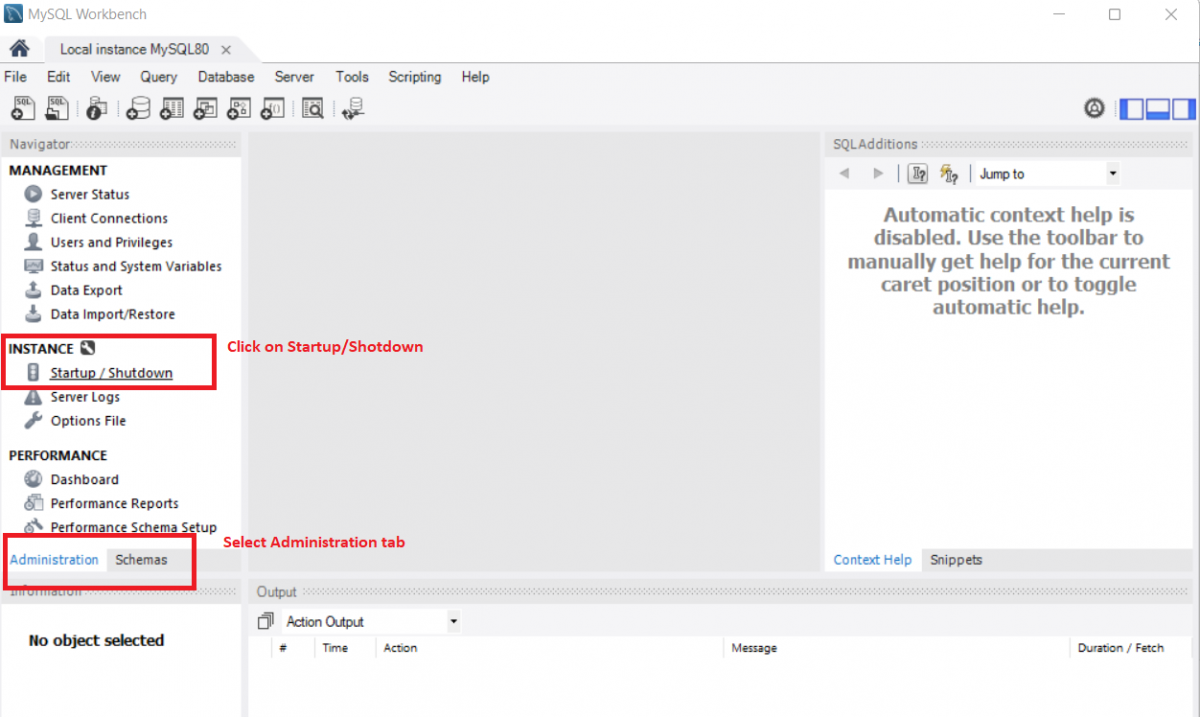
Step 2: Select the Administrator tab, in the Instances section select the Startup/Shutdown section.
Step 3: You can start or stop the server in this window.
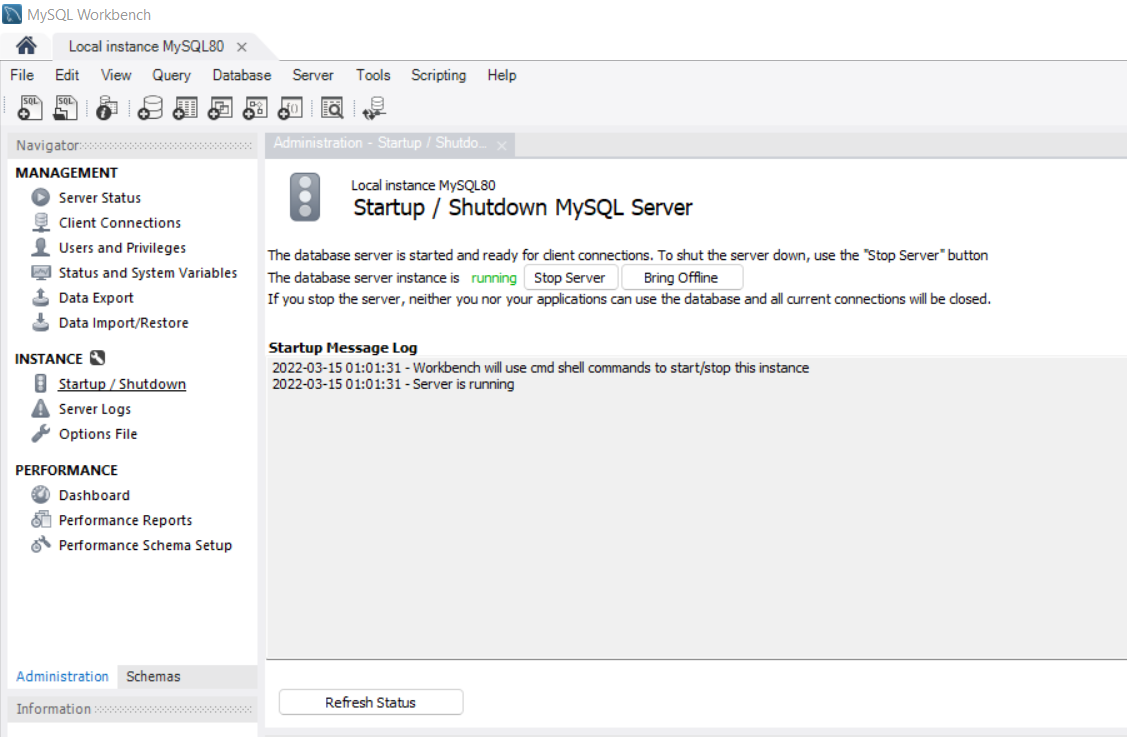
These are the three ways, you can use to start or stop of MySQL server.
Start, Stop and restart MySQL Server on Linux
For performing these activities on Linux, you must be a superuser as only the superuser has these privileges.
Step 1: Open your Linux terminal and we need to check if MySQL is running on your operating system or not. To do so, we’ll need to type the following command:
service mysqld statusCode language: Bash (bash)If MySQL is properly configured on your OS then the command will return Active status as Active(running) which means that MySQL is running on your operating system.
Step 2: Start, stop or restart MySQL
There will be two commands, service and sudo, both should work properly, but it depends if you have the privilege to use the service or sudo command on Linux. Make sure that you are a root user or a super user to perform the activity on MySQL.
To stop the MySQL server on Linux, use the following command:
service mysqld stop
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stopCode language: Bash (bash)The above command will stop the MySQL server. Now if you will try to check again for the MySQL status it will show inactive(dead) on the active status.
To Start the MySQL server on Linux, use the following command:
service mysqld start
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql startCode language: Bash (bash)The above command will start the MySQL server. Now, if you will try to check again for the MySQL status it will again be active(running) on the active status.
To restart the MySQL server on Linux, use the following command:
service mysqld restart
sudo /etc/init.d/mysql restartCode language: Bash (bash)The above command will restart the MySQL server. Now, if you will try to check again for the MySQL status it will again be active(running) on the active status because we restarted the server.
Start, Stop or Restart MySQL Server on macOS
Open terminal on your Mac, we’ll be using the Sudo command to start, stop or restart the MySQL server.
For MySQL versions which are newer than 5.7:
To start MySQL server on Mac:
sudo launchctl load -F /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.oracle.oss.mysql.mysqld.plistCode language: Bash (bash)To Stop MySQL server on Mac:
sudo launchctl unload -F /Library/LaunchDaemons/com.oracle.oss.mysql.mysqld.plistCode language: Bash (bash)For versions older than MySQL 5.7:
To Start MySQL server on Mac:
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server startCode language: Bash (bash)To Stop MySQL server on Mac:
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server stopCode language: Bash (bash)To Restart MySQL server on Mac:
sudo /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server restartCode language: Bash (bash)Conclusion
Mysql is a powerful database management system. In order to use it effectively, you need to be familiar with the different ways to start, stop and restart it. By following the instructions in this article, you should be able to do just that. Thank you for reading!
