In this tutorial, we will study the MySQL UTC_TIME(), UTC_DATE() and UTC_TIMESTAMP() functions. Coordinated Universal Time or UTC is the primary time standard by which the world regulates clocks and time.
It is within about 1 second of mean solar time at 0° longitude, and is not adjusted for daylight saving time.
It is effectively a successor to Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). Suppose you want to find the UTC time in MySQL. This is where you use the UTC_TIME() function.
Furthermore, we also have UTC_DATE() and UTC_TIMESTAMP() functions. Let us take a look at this.
- The
UTC_TIME()function is used to return the current UTC time. - The
UTC_DATE()function is used to return the current UTC date. - The
UTC_TIMESTAMP()function is used to return the current UTC datetime value.
Let us take a look at the syntax and example of each of them.
Syntax of MySQL UTC_TIME()
UTC_TIME([fsp])Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Or
UTC_TIMECode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Where,
‘fsp’ is an optional parameter that states the fractional seconds precision for the time value to be returned.
Syntax of MySQL UTC_DATE()
UTC_DATE()Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Or
UTC_DATECode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Syntax of MySQL UTC_TIMESTAMP()
UTC_TIMESTAMP([fsp])Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Or
UTC_TIMESTAMPCode language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Where,
‘fsp’ is an optional parameter that states the fractional seconds precision for the datetime value to be returned.
Examples of MySQL UTC_TIME()
Let us start with the MySQL UTC_TIME() function. Here is how we can display the current UTC time using the SELECT statement.
SELECT UTC_TIME(); Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output is –
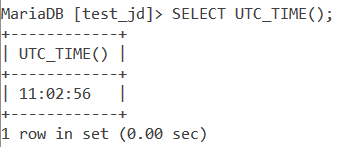
We can also do it without the parentheses as follows –
SELECT UTC_TIME;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output is –
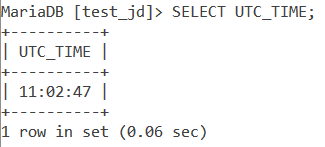
Displaying Fractional Seconds Precision of the current UTC time.
We can display the UTC time value upto 6 fractional seconds precision. In this case, we need to specify the ‘fsp’ parameter. The ‘fsp’ parameter can have a value from 1 to 6. Let us see an example of this.
SELECT UTC_TIME(6);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output is –
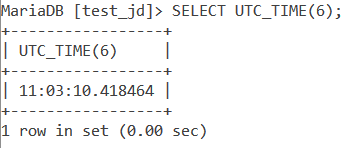
MySQL UTC_TIME() in Numerical Context
In the above examples, we got the time in the HH:MM:SS format. This is because the time value was returned as a string. To return the time value in a numerical context, we add a “+ 0” to it. Here is an example of this.
SELECT UTC_TIME() + 0;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output is –
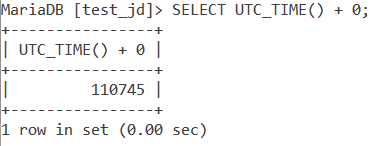
Examples of MySQL UTC_DATE()
Next, let us move on with the UTC_DATE() function. Here are the two ways you can display the current UTC date using the SELECT statement. The queries are –
SELECT UTC_DATE;
SELECT UTC_DATE();Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output is –

UTC Date in Numerical Context
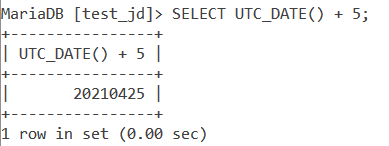
In the above example, we got the date in the ‘YYYY-MM-DD’ format. This is because the date value was returned as a string. To return the date value in a numerical context, we add a “+ 0” to it. In the below example we add “+ 5” to the UTC_DATE() function. This returns the numerical value for the date 5 days after the current UTC date.
SELECT UTC_DATE() + 5;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output is –
Examples of MySQL UTC_TIMESTAMP()
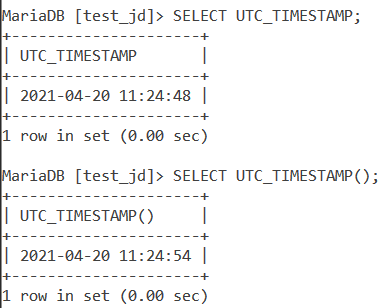
Finally, let us see examples of the UTC_TIMESTAMP() function. Here are the two ways you can display the current UTC datetime value using the SELECT statement. The queries are –
SELECT UTC_TIMESTAMP;
SELECT UTC_TIMESTAMP();Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output is –
Displaying Fractional Seconds Precision of the current UTC datetime value.
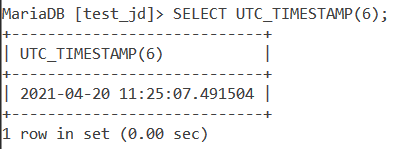
We can display the UTC datetime value upto 6 fractional seconds precision. In this case, we need to specify the ‘fsp’ parameter. The ‘fsp’ parameter can have a value from 1 to 6. Let us see an example of this.
SELECT UTC_TIMESTAMP(6);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output is –
UTC datetime value in Numerical Context
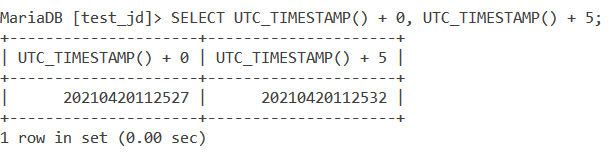
In the above examples, we got the datetime in the ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS’ format. This is because the datetime value was returned as a string. To return the datetime value in a numerical context, we add a “+ 0” to it. Here is an example of this.
SELECT UTC_TIMESTAMP() + 0, UTC_TIMESTAMP() + 5;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output is –
Conclusion
So that was a roundup on how we display the UTC time, date and timestamp using MySQL. I hope you liked this article. Do check out the below references.
References
- MySQL Official Documentation on UTC_DATE(), UTC_TIME() and UTC_TIMESTAMP() functions.
