In this tutorial, we will take a look at the MySQL IS NULL condition. Suppose you are conducting a survey in your neighborhood and you hand out a small questionnaire to everyone in the area.
After a day or two, you receive the questionnaires back and you notice that some people have not answered a few questions and left them blank instead. These blank datapoints are completely useless for any sort of data analysis as they can skew our averages.
So how do we identify all the null values from a set of data? The MySQL IS NULL condition can help!
What is a NULL value?
In MySQL, you may come across situations like this. It may happen that some records may not have a value at all. The SQL NULL term is used to represent such missing values.
If a field has a NULL value, it means that it has no value. NULL is not the same as 0 or a string with space.
In both cases, there is a value. Both the number 0, and the single space, can be represented as unicode characters. So we cannot consider them as absence of data.
NULL is used to represent a complete absence of any value whatsoever.
Missing values can be a problem in large tables and may give you weird errors at times. So, how do we check for them in a table? We cannot use comparison operators like = and != for checking a NULL value in MySQL.
In MySQL, we check for a NULL value in a table using the IS NULL condition along with the WHERE clause.
Syntax for the IS NULL condition
SELECT expression FROM table_name WHERE column_name IS NULL;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Example of the MySQL IS NULL condition
Consider the following table Employee table.
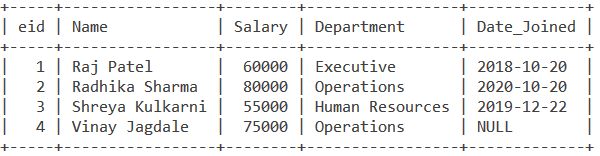
1. Finding NULL values
Let us find if the name column has any NULL values using the SELECT statement. We do so with the following query,
SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE Name IS NULL;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)We get the output as,
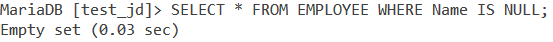
Empty set means that the result-set for this query is empty. This means that the Name column does not have a NULL value.
Let us now try to check the NULL values in the Date_Joined column. We do so using the following query,
SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE Date_Joined IS NULL;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The output is,

As you can see, the Date_Joined field for Vinay Jagdale (eid = 4) is NULL. It may have happened that while entering his record in the table, someone might have missed putting in that value.
2. Updating NULL Values
After finding a NULL value, you may wish to update it to a meaningful value. To do this, we use the UPDATE statement.
UPDATE Employee SET Date_Joined='2020-10-30' WHERE Date_Joined IS NULL;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)We will get the output as,
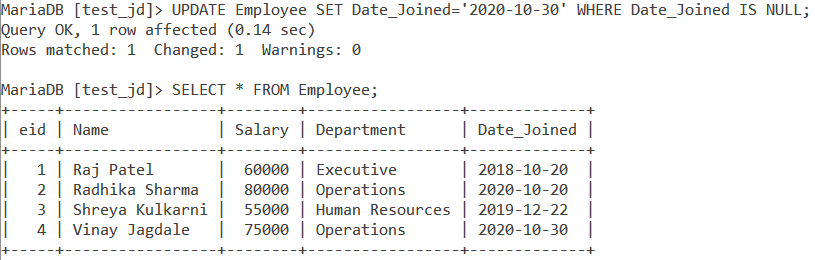
As you can see, the NULL value in the Date_Joined column gets updated.
3. Deleting Columns With NULL Values
Conversely, you can also use the DELETE statement to find the NULL values in a table and get them deleted instead of updating it to a value.
So let us consider the initial Employee table i.e. before we updated the NULL value. To delete a record with a NULL value, we use the following query:
DELETE FROM Employee WHERE Date_Joined IS NULL;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)We will get the output as follows:
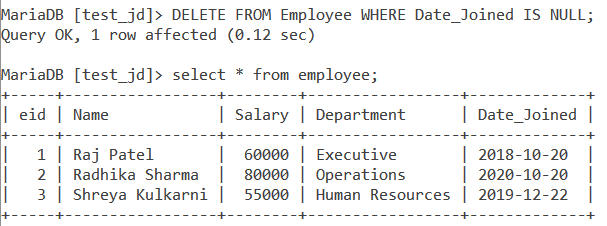
As you can see, the entry containing the NULL value got deleted from the table.
Conclusion
In larger tables, NULL values can create a lot of problems, especially during any form of computation. Detecting and handling NULL values using the MySQL IS NULL condition is a very important step in data cleaning.
References
- MySQL official documentation on IS NULL condition.
- JournalDev article on IS NULL condition.
