In this tutorial, we will take a look at the MySQL IS NOT NULL condition. IS NOT NULL condition is the exact opposite of the IS NULL condition. IS NOT NULL filters through the table for a column and returns only those records who do not have a NULL value in that particular column. This condition is often used with the WHERE clause.
As mentioned in the IS NULL condition article, missing values can be a problem in large tables, resulting in errors during computations. Also, we cannot use comparison operators like = and != for checking a NULL value in MySQL.
Syntax for the IS NOT NULL condition
SELECT expression FROM table_name WHERE column_name IS NOT NULL;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Example of the MySQL IS NOT NULL condition
Consider the following table Employee table.
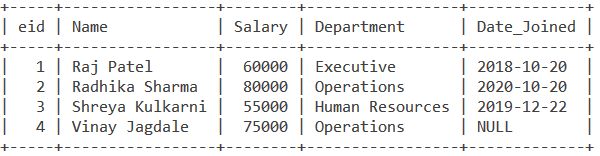
1. Using IS NOT NULL to find non-NULL values
Let us find out the non-NULL values in the Date_Joined column using the SELECT statement. We do so with the following query,
SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE Date_Joined IS NOT NULL;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)We get the output as,
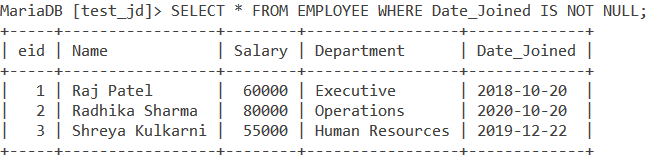
As you can see, the first three entries in the table did not have a NULL value in the Date_Joined column and hence we get them in our result.
In case a particular column has all NULL values, then we get an Empty set in the result-set.
2. Using IS NOT NULL to update non-NULL values
You can update non-NULL values using the IS NOT NULL condition along with the UPDATE statement. The query is,
UPDATE Employee SET Date_Joined='2020-11-01' WHERE Date_Joined IS NOT NULL;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)This will filter all values that are not NULL in the Date_Joined column and set their value to ‘2020-11-01’. We will get the output as,
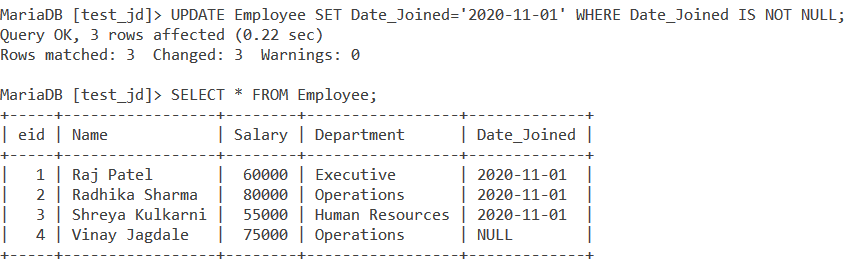
You can also use the DELETE statement along with the IS NOT NULL condition in the same way as we use it for the IS NULL condition. From a practical point of view, you don’t delete non-NULL value records most of the time as opposed to the NULL value records.
Conclusion
In larger tables, IS NOT NULL condition can be very useful in extracting only the non-NULL values and performing computation on them. For further reading, I would highly recommend you to go through the links in the references.
References
- MySQL official documentation on
IS NOT NULLcondition. - JournalDev article on
IS NOT NULLcondition.
