In this tutorial, we will study the MySQL GROUP BY clause. The MySQL GROUP BY clause collects data from multiple rows and groups the rows into subgroups based on their value. GROUP BY is usually used with the SELECT statement. As you proceed with this tutorial and in the world of databases, you will notice that aggregate functions are prominently used along with the GROUP BY clause.
Syntax for MySQL GROUP BY
SELECT expressions FROM table_name [WHERE conditions] GROUP BY column_name(s);Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Note that you may include other clauses or even subqueries in the above syntax.
Examples of MySQL GROUP BY
Consider the below Employee table.
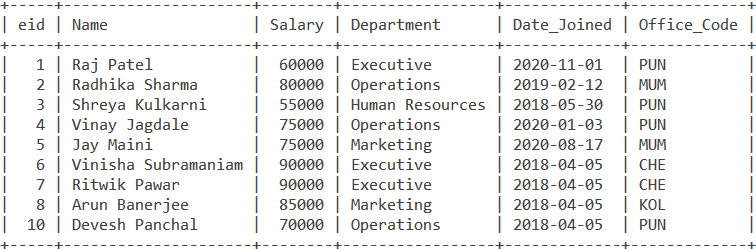
Simple Example using GROUP BY
Let us start with a simple example first. How about grouping the values of the Department column into subgroups? We use the below query,
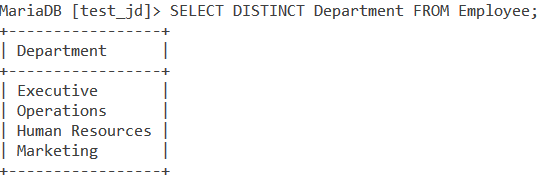
SELECT Department FROM Employee GROUP BY Department;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And we get the output as,

You will notice that there is another way to get the same output. If we use the DISTINCT keyword, we will get the same output. In that case, the query is,
SELECT DISTINCT Department FROM Employee;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output is the same as what we get with the GROUP BY query above.
Using GROUP BY With Aggregate Functions
GROUP BY is prominently used with all the aggregate functions. We will see how GROUP BY is used with a few of these Aggregate Functions.
Using COUNT()
How about finding the number of employees in each department? We will use the aggregate function COUNT() for this.
SELECT Department, COUNT(*) FROM Employee GROUP BY Department;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And we get the output as follows,
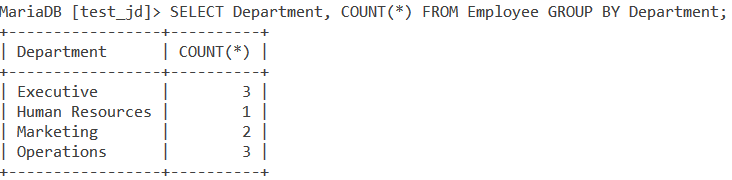
Two columns are formed in the result as specified by us in the query. The first column tells us the Department names and the second column tells us the number of employees in that particular department.
With MAX()
Now let us use the MAX() function with GROUP BY. How about finding the highest salary in each department? We use the following query,
SELECT Department, MAX(Salary) FROM Employee GROUP BY Department;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output we get is,
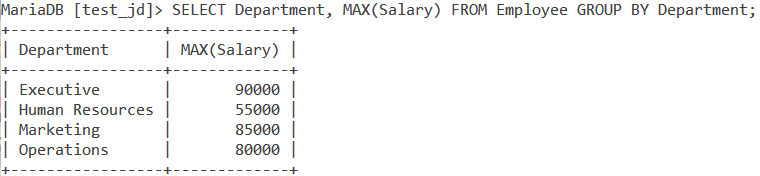
With AVG()
Lastly, let us see an example of how the AVG() function works with GROUP BY. Let us find the average salary for each office and group it in our result-set. We use the following query for the operation,
SELECT Office_Code, AVG(Salary) FROM Employee GROUP BY Office_Code;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)The output is,

Using GROUP BY With The IN Operator
Let us see a complex example now. Let us find out the number of employees in the offices with codes ‘MUM’ and ‘PUN’ and group it in our result-set. We will use the WHERE clause and IN operator for this.
SELECT Office_Code, Count(*) FROM Employee WHERE Office_Code IN ('MUM', 'PUN') GROUP BY Office_Code;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And we get the output as follows,

Conclusion
Just like the aggregate functions, GROUP BY proves useful in data analysis. GROUP BY clause is like an added layer for effective querying with tables. For more information, do check out the links below.
References
- MySQL Official documentation on
GROUP BY.
