In this tutorial, we will learn about the MySQL UNION operator. Suppose you encounter a situation in which you need to combine the results of two different queries. What would you do in such a case? MySQL provides us with the UNION operator for this purpose. MySQL UNION is used to combine the result-set of two or more SELECT statements into a single result-set.
MySQL UNION works just like the union operator you must have studied in Sets in high school maths. MySQL UNION comes with certain restrictions though. They are:
- Each
SELECTstatement used with theUNIONoperator must have the same number of columns. - The columns mentioned in the
SELECTStatement’s expression must have similar data types. - The columns mentioned in the
SELECTStatement’s expression must be in the same order as the otherSELECTstatements.
Syntax of MySQL UNION
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name1 UNION SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name2;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)Examples of MySQL UNION
Consider the below Employee and Office tables.
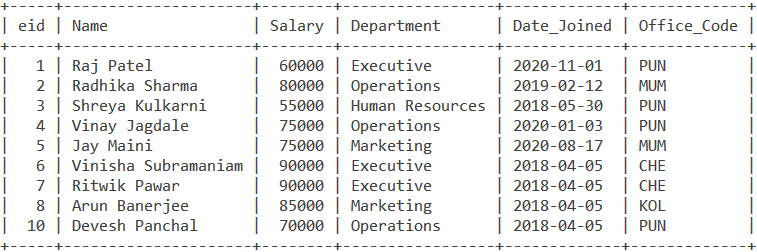
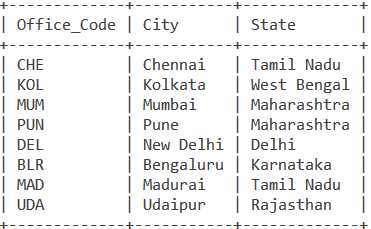
Simple Example of MySQL UNION
Now let us return the office code values from both the ‘Employee’ and ‘Office’ tables. We do so using the query,
SELECT Office_Code FROM Employee UNION SELECT Office_Code FROM Office;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And we get the output as follows,
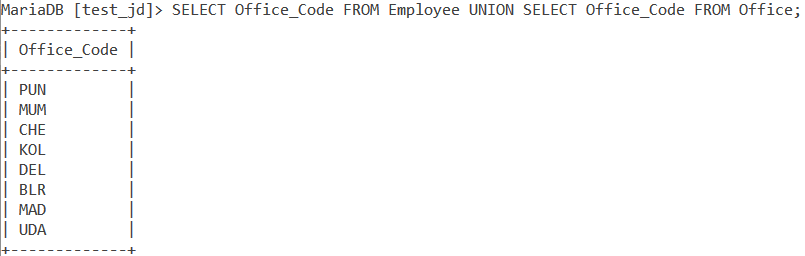
Note that MySQL UNION only returns the distinct values of the column that was mentioned.
MySQL UNION with ALL
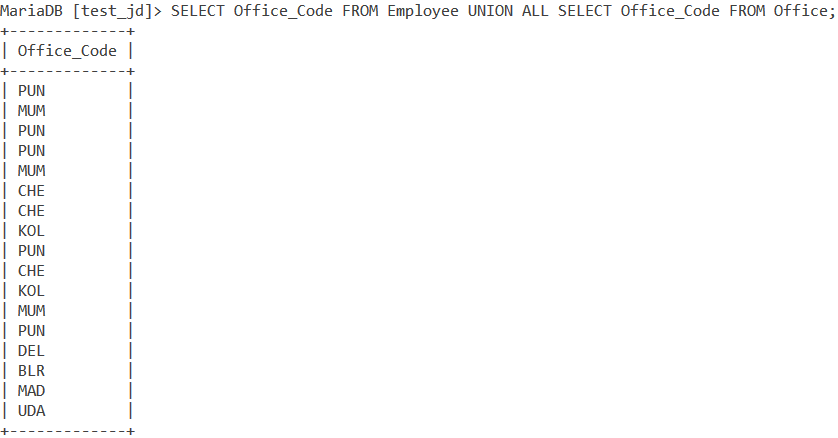
To get the duplicate values in the result-set of the UNION operation, we use MySQL UNION ALL. Let me demonstrate using the following query.
SELECT Office_Code FROM Employee UNION ALL SELECT Office_Code FROM Office;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)This query returns the office code values, including duplicate ones from both the tables. We get our output as,
MySQL UNION With WHERE Clause And Subqueries
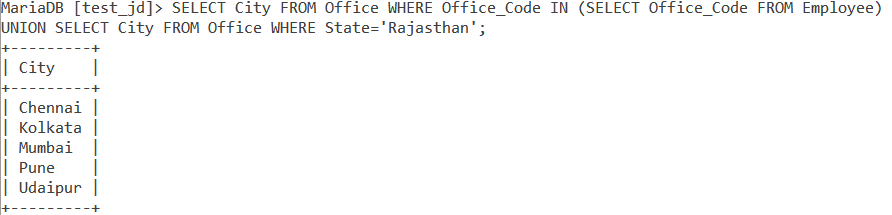
Let us take a complex example now by using Subqueries and the WHERE clause with the UNION operator. How about finding distinct city names from both the tables provided that we include all city names from the Employee table and only cities from the state of Rajasthan from the Office table?
SELECT City FROM Office WHERE Office_Code IN (SELECT Office_Code FROM Employee) UNION SELECT City FROM Office WHERE State='Rajasthan';Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And we get our output as,
Conclusion
MySQL UNION proves very useful with complex queries involving large tables. The ability to merge two result-sets can be very useful depending on our use cases. I would recommend you to check out the references.
References
- MySQL Official Documentation on the
UNIONoperator. - JournalDev article on MySQL
UNION.
