In this tutorial, we will study the MySQL DATE_ADD() and DATE_SUB() functions. DATE_ADD() and DATE_SUB() are a variation of the ADDDATE() and SUBDATE() functions. The main difference is that DATE_ADD() and DATE_SUB() only have one syntax each, not two syntaxes like ADDDATE() and SUBDATE().
- The
DATE_ADD()function is used to add a date or time interval to a date/datetime value. - The
DATE_SUB()function is used to subtract a date or time interval from a date/datetime value.
Let us take a look at their syntax and see a couple of examples.
Syntax for MySQL DATE_ADD() and DATE_SUB()
For DATE_ADD() –
DATE_ADD(date, INTERVAL value interval_type)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)For DATE_SUB() –
DATE_SUB(date, INTERVAL value interval_type)Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)In both the above syntaxes,
- date’ is the date/datetime value to be modified,
- ‘value’ is the value of the time interval to be added and,
- ‘interval_type’ is the type of interval to be added.
The ‘interval_type’ parameter can have the below values –
- MICROSECOND
- SECOND
- MINUTE
- HOUR
- DAY
- WEEK
- MONTH
- QUARTER
- YEAR
The below ‘interval_type’ values should be in quotes.
- SECOND_MICROSECOND where value is of the format – ‘SECONDS.MICROSECONDS’
- MINUTE_MICROSECOND where value is of the format – ‘MINUTES:SECONDS.MICROSECONDS’
- MINUTE_SECOND where value is of the format – ‘MINUTES:SECONDS’
- HOUR_MICROSECOND where value is of the format – ‘HOURS:MINUTES:SECONDS.MICROSECONDS’
- HOUR_SECOND where value is of the format – ‘HOURS:MINUTES:SECONDS’
- HOUR_MINUTE where value is of the format – ‘HOURS:MINUTES’
- DAY_MICROSECOND where value is of the format – ‘DAYS HOURS:MINUTES:SECONDS.MICROSECONDS’
- DAY_SECOND where value is of the format – ‘DAYS HOURS:MINUTES:SECONDS’
- DAY_MINUTE where value is of the format – ‘DAYS HOURS:MINUTES’
- DAY_HOUR where value is of the format – ‘DAYS HOURS’
- YEAR_MONTH where value is of the format – ‘YEARS-MONTHS’
Examples of MySQL DATE_ADD() and DATE_SUB()
Let us start with a couple of basic examples. Let us start with the DATE_ADD() function. We have the following date value – ‘2015-06-15’. In the first query, let us add 5 years to it. In the second query, let us add 6 months to it. We will use the SELECT statement and an alias called Result. The queries are –
SELECT DATE_ADD('2015-06-15', INTERVAL 5 YEAR) AS Result;
SELECT DATE_ADD('2015-06-15', INTERVAL 6 MONTH) AS Result;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output is –
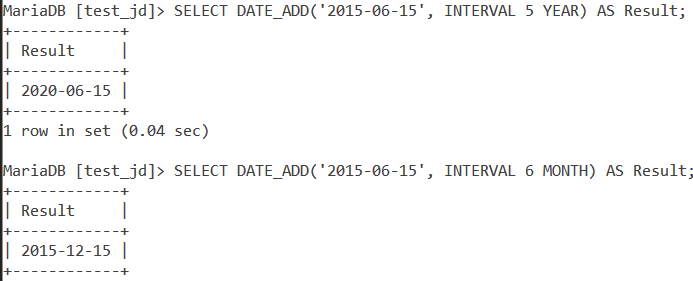
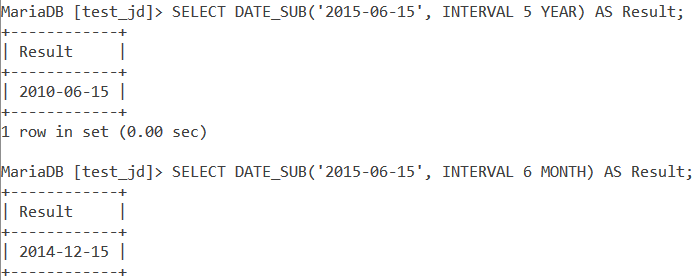
Next, let us look at a basic example of DATE_SUB(). For the same date value, let us write two queries. The first one should subtract 5 years while the second query should subtract 6 months from the date value. The queries are –
SELECT DATE_SUB('2015-06-15', INTERVAL 5 YEAR) AS Result;
SELECT DATE_SUB('2015-06-15', INTERVAL 6 MONTH) AS Result;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output is –
Using NOW() with DATE_ADD() and DATE_SUB()
Let us use the MySQL NOW() function with DATE_ADD() function. How about we add a quarter to the current datetime value. The query is –
SELECT DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL 1 QUARTER) AS Result; Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output is –
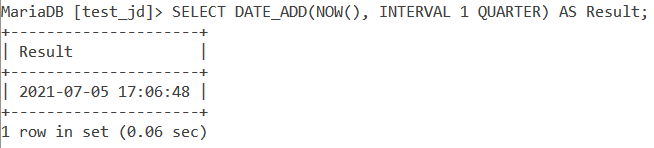
Similarly, let us subtract 3 quarters from the current datetime value using the DATE_SUB() function. The query is –
SELECT DATE_SUB(NOW(), INTERVAL 3 QUARTER) AS Result;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output is –

Miscellaneous Example
Let us solve the below problem.
You have the following datetime value – ‘2021-02-14 12:05:00’. Write a query using the DATE_ADD() function that adds 5 days and 10 hours to it.
In the second query, use the DATE_SUB() function to subtract 6 hours, 25 minutes seconds and 004000 microseconds from the given datetime value. The queries are –
SELECT DATE_ADD('2021-02-14 12:05:00', INTERVAL '5 10' DAY_HOUR) AS Result;
SELECT DATE_SUB('2021-02-14 12:05:00.1256', INTERVAL '06:25:05.004' HOUR_MICROSECOND) AS Result;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output is –

Working With Tables
Consider the below BusStop table.
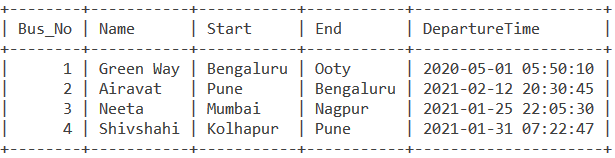
Due to a snowstorm, all buses have been delayed by 3 days. Let us use the DATE_ADD() function to display the bus details and the new departure time. The query is –
SELECT Bus_No, Name, Start, End, DATE_ADD(DepartureTime, INTERVAL 3 DAY) AS 'New Departure Time' FROM BusStop;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output is –
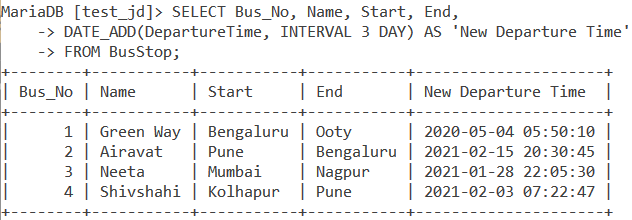
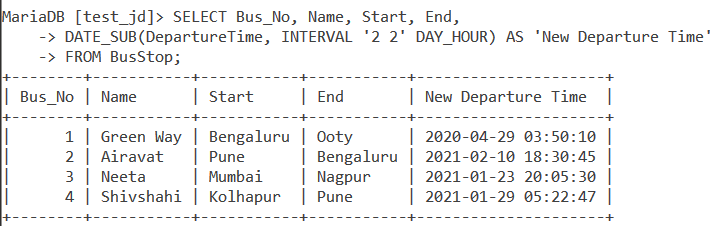
Let also write a query that subtracts 2 days and 2 hours from the departure time for each bus. Let us display the bus details and the new departure time. The query is –
SELECT Bus_No, Name, Start, End, DATE_SUB(DepartureTime, INTERVAL '2 2' DAY_HOUR) AS 'New Departure Time' FROM BusStop;Code language: SQL (Structured Query Language) (sql)And the output is –
Conclusion
The MySQL DATE_ADD() and DATE_SUB() functions are very useful. Basic addition and subtraction operations on date and datetime values are very important and have a plethora of use cases. I would encourage you to practice some more queries with this function.
References
- MySQL Official Documentation on the
DATE_ADD()andDATE_SUB()functions.
